|
Classes | |
| class | BaseMobility |
| Base module for all mobility modules. More... | |
| class | ANSimMobility |
| Uses the <position_change> elements of the ANSim tool's trace file. See NED file for more info. More... | |
| class | BonnMotionFile |
| class | BonnMotionFileCache |
| class | BonnMotionMobility |
| Uses the BonnMotion native file format. See NED file for more info. More... | |
| class | CircleMobility |
| Circle movement model. See NED file for more info. More... | |
| class | ConstSpeedMobility |
| Controls all movement related things of a host. More... | |
| class | LinearMobility |
| Linear movement model. See NED file for more info. More... | |
| class | LineSegmentsMobilityBase |
| Base class for mobility models where movement consists of a sequence of linear movements of constant speed. More... | |
| class | MassMobility |
| Models the mobility of with mass, making random motions. See NED file for more info. More... | |
| class | MoBANCoordinator |
| This is the coordinator module of the MoBAN mobility model. It should be instantiated in the top level simulation network in MiXiM, once per WBAN. The coordinator module is the main module that provides the group mobility and correlation between nodes in a WBAN. In the initialization phase, it reads three user defined input files which are the postures specification file, a configuration file which includes all required parameter for specific distributions, and the previously logged mobility pattern, if it is requested to use a logged pattern. Note that all WBAN instances may use the same input files if they are exactly in the same situation. More... | |
| class | MoBANLocal |
| This is the local mobility module of MoBAN. It should be instantiated in each node that belongs to a WBAN. The NED parameter "coordinatorIndex" determine to which WBAN (MoBANCoordinator) it belongs. The current implementation uses the Random Walk Mobility Model (RWMM) for individual (local) movement with a sphere around the node, with given speed and sphere radius of the current posture. The reference point of the node it the current posture, the sphere radius, and the speed is given by the corresponding coordinator through the blackboard. RWMM determines the location of node at ant time relative to the given reference point. More... | |
| class | Posture |
| to store the specification of a posture on the MoBAN mobility model. More... | |
| class | PostureTransition |
| Class to provide spatial and temporal correlation in the posture selection process of the MoBAN mobility model. This class obtains and stores Markovian transition matrices. There is also the possibility to get a steady state vector. In this case, the closest transition matrix to the default Makov matrix is extracted which satisfies the given steady state vector. The class also receives the defined area types and time domains as well as given space-time domains during the initialization phase. During the simulation run, the class provide a functions to return the corresponding markov matrix for a given time and location. It will be used whenever a new posture is going to be selected. More... | |
| class | RectangleMobility |
| Rectangle movement model. See NED file for more info. More... | |
| class | TractorMobility |
| Tractor movement model. See NED file for more info. More... | |
| class | TurtleMobility |
| LOGO-style movement model, with the script coming from XML. See NED file for more info. More... | |
Detailed Description
The following diagrams give an overview of the functionality of a mobility-module.
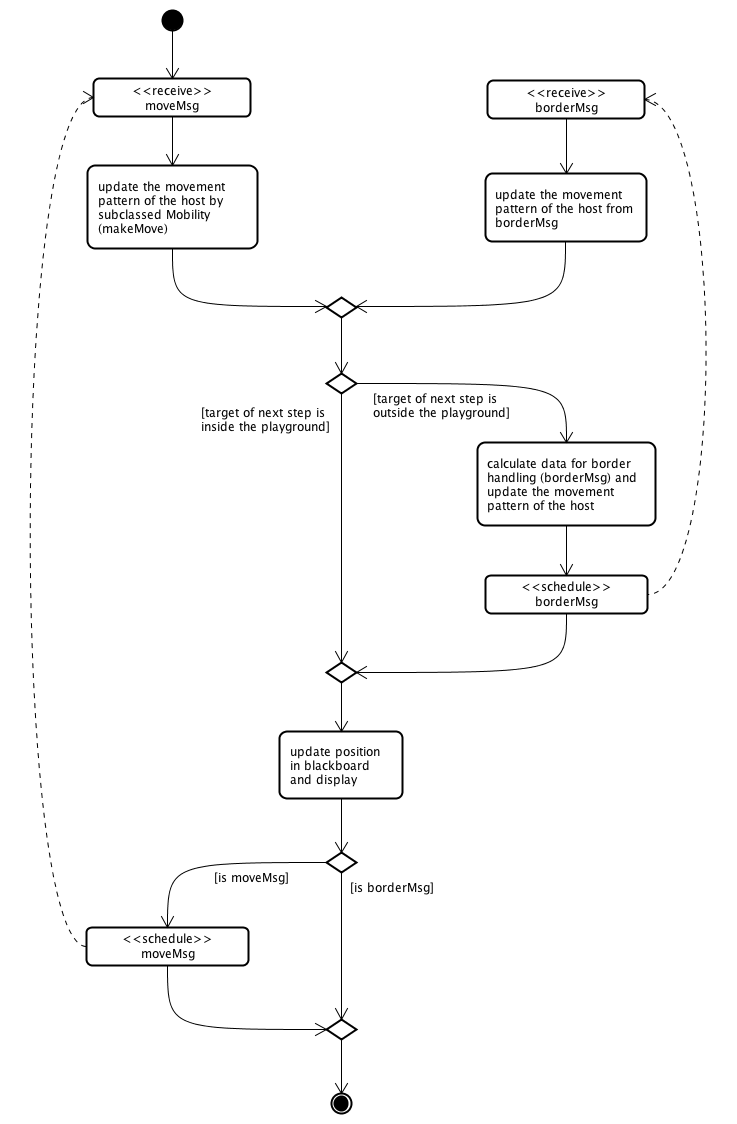
Activity diagram: an overview on how movement-updates in BaseMobility work
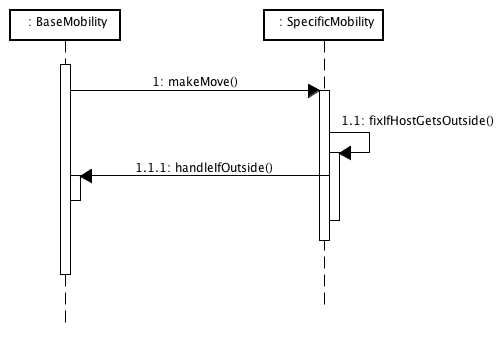
Sequence diagram: call-hierarchy when move-message is processed
Shows how sub-classing mobility-modules are involved in the movement-calculation for a host. They overwrite the method makeMove() to calculate the next movement-step and after that they have to call fixIfHostGetsOutside() which takes care of border-handling. The implementation of this method at least has to call handleIfOutside() and pass the border-policy to use as well as references to parameters to be updated. The figure below shows some details on how border-handling and the different border-policies work.
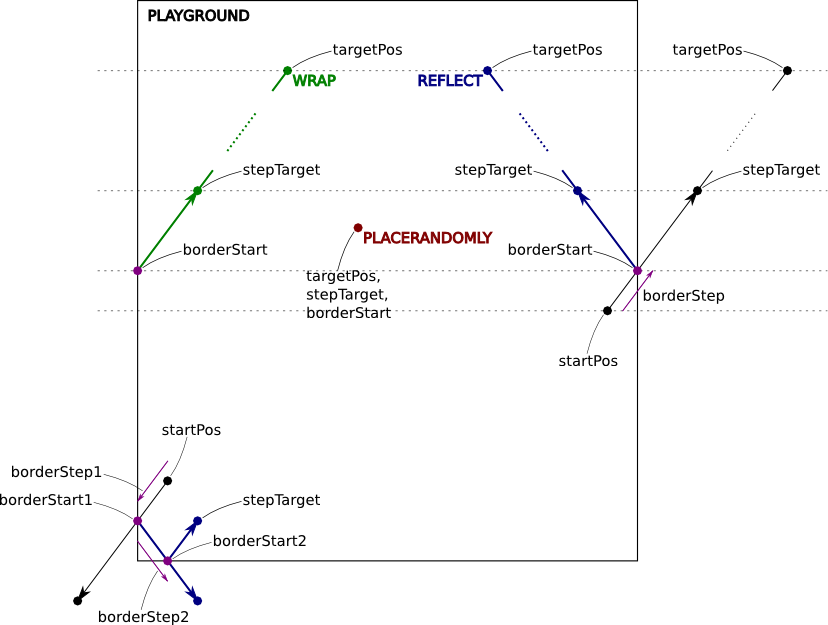
Illustrated border-handling under the different border-policies, multiple border-handling in one movement-step
 1.7.1
1.7.1