 This documentation is released under the Creative Commons license
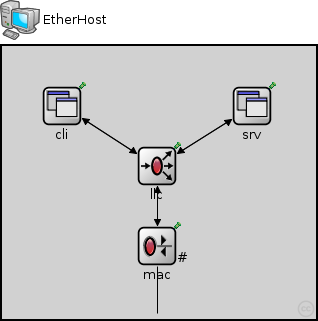
This documentation is released under the Creative Commons licenseAn example host with one Ethernet port and traffic generators that generate Ethernet traffic directly. This host model does not contain higher layer protocols (IP, TCP).
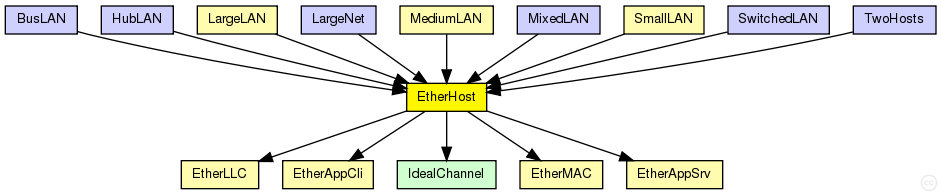
The following diagram shows usage relationships between types. Unresolved types are missing from the diagram. Click here to see the full picture.
The following diagram shows inheritance relationships for this type. Unresolved types are missing from the diagram. Click here to see the full picture.

If a module type shows up more than once, that means it has been defined in more than one NED file.
| LargeLAN (compound module) |
Several hosts and an Ethernet hub on a switch. One port of the hub connect to a 10Base2 segment. |
| MediumLAN (compound module) |
Several hosts and an Ethernet hub on a switch |
| SmallLAN (compound module) |
Several hosts on an Ethernet hub |
| BusLAN (network) |
Sample Ethernet LAN: four hosts on a bus. |
| HubLAN (network) |
Sample Ethernet LAN: four hosts connected by a hub. |
| LargeNet (network) |
A large Ethernet LAN -- see model description here. |
| MixedLAN (network) |
Sample Ethernet LAN containing eight hosts, a switch and a bus. |
| SwitchedLAN (network) |
Sample Ethernet LAN: four hosts connected to a switch. |
| TwoHosts (network) |
Sample Ethernet LAN: two hosts directly connected to each other via twisted pair. |
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| node | ||
| labels | node | |
| display | i=device/pc2 |
| Name | Direction | Size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ethg | inout |
| Name | Type | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| cli.destAddress | string | "" |
destination MAC address, or module path name of destination station; empty means off |
| cli.startTime | double | this.waitTime |
time of sending the first request |
| cli.waitTime | double | uniform(0s,1s) |
interval between sending requests |
| cli.reqLength | int | 100B |
length of request packets |
| cli.respLength | int | 1KB |
length of response packets |
| mac.promiscuous | bool | false |
if true, all packets are received, otherwise only the ones with matching destination MAC address |
| mac.address | string | "auto" |
MAC address as hex string (12 hex digits), or "auto". "auto" values will be replaced by a generated MAC address in init stage 0. |
| mac.txrate | double | 100Mbps |
maximum data rate supported by this station (bit/s); actually chosen speed may be lower due to auto- configuration. 0 means fully auto-configured. |
| mac.duplexEnabled | bool | true |
whether duplex mode can be enabled or not; whether MAC will actually use duplex mode depends on the result of the auto-configuration process (duplex is only possible with DTE-to-DTE connection). |
| mac.txQueueLimit | int | 1000 |
maximum number of frames queued up for transmission; additional frames are dropped. Only used if queueModule=="" |
| mac.mtu | int | 1500 |
// // An example host with one Ethernet port and traffic generators that // generate Ethernet traffic directly. This host model does not contain // higher layer protocols (\IP, \TCP). // module EtherHost { parameters: @node(); @labels(node,ethernet-node); @display("i=device/pc2"); gates: inout ethg @labels(EtherFrame-conn); submodules: cli: EtherAppCli { parameters: registerSAP = true; @display("p=60,60,col"); } srv: EtherAppSrv { parameters: registerSAP = true; @display("p=250,60,col"); } llc: EtherLLC { parameters: @display("p=155,120"); gates: upperLayerIn[2]; upperLayerOut[2]; } mac: EtherMAC { parameters: queueModule = ""; @display("p=155,200;q=queue"); } connections: llc.lowerLayerIn <-- mac.upperLayerOut; llc.lowerLayerOut --> mac.upperLayerIn; mac.phys <--> ethg; cli.out --> llc.upperLayerIn[0]; cli.in <-- llc.upperLayerOut[0]; srv.out --> llc.upperLayerIn[1]; srv.in <-- llc.upperLayerOut[1]; }